Posts filed under ‘Creative People’
Wolfgang Amadeus Mozart a Musical Genius
full baptismal name Johannes Chrysostomus Wolfgangus Theophilus Mozart
(27 January 1756, Salzburg, Austria – 5 December 1791, Vienna, Austria)
Nationality: Austria
Category: Art workers
Occupation: Composer
Specification: One of the great figures in the history of music. He is considered as a musical genius, one of the most significant and influential of all classical composers. Classical music.
Gender: Male
Personal life: His mother -Anna Maria Pertl, and father Leopold Mozart, who was composer, concertmaster and an experienced teacher.
Mozart Together with his older sister, Maria Anna, nicknamed “Nannerl”, received intensive musical training from his father. A child prodigy, Mozart at the age of three learned compositions from his father and started to play the keyboard, at age four perfected ballads, at age five he composed his first minuets, had his first piece published when he was eight and wrote his first opera when he was twelve.
On August 4, 1782, he married Constanze Weber against his father’s wishes and they had 6 children, but only two (sons) survived.
Mozart mainly lived in Salzburg and Vienna and during his short life of only 35 years completed several long concert tour throughout Europe, which included stays in Paris, London, Milan, Rome and Prague. At the beginning of his musical career, he played with his father and sister for Louis XV at Versailles and George III in London. During his trips, he met such great composers as J.S. Bach, G.F. Handel, and Joseph Haydn. He taught and gave piano lessons to make ends meet. He enjoyed dancing, joking and playing billiard. Mozart died on 5 December 1791 at the aged of 35. Some have speculated that Mozart was poisoned by rival composer Antonio Salieri, but no proof exists to support that theory. Mozart probably died of rheumatic fever.
Creative style: Mozart had the unique and universal creative style, that formed on the basis of his ability to incorporate many musical elements and style and absorbe, adapt valuable features of others’ music Including
the Baroque. Mozart possessed an powerful musical memory, excellent ability to improvisation, holistic perception and playful attitude towards the world.
Genres: Mozart was a versatile composer, and wrote in every major genre: chamber music, symphonies, operas, Masses.
He mainly wrote Operas, Church Music, Vocal and Choral Music, Orchestral Music, Chamber Music, Piano Music and Organ Music, concert arias and scenes.
Major works: He was also a very prolific composer and composed over 600 works including:21 stage and opera works, 15 Masses, over 50 symphonies, 30 keyboard, 25 piano and 12 violin concertos, dances and sets of dances. His major works are the operas Le Nozze di Figaro (The Marriage of Figaro, 1786), Don Giovanni,1787 and Die Zauberflöte, (The Magic Flute, 1791); comic masterpiece the short work for orchestra Eine Kleine Nachtmusik (A Little Night Music, 1787) and his last three church pieces: Ave Verum Corpus, 1791, Mass in C Minor, and Requiem (Both remain unfinished).
Mozart Quotes:
1. Music is my life and my life is music.
2. Neither a lofty degree of intelligence nor imagination nor both together go to the making of genius. Love, love, love, that is the soul of genius.
3. The music is not in the notes, but in the silence between.
4. When I am ….. completely myself, entirely alone… or during the night when I cannot sleep, it is on such occasions that my ideas flow best and most abundantly. Whence and how these ideas come I know not nor can I force them.
5. Nor do I hear in my imagination the parts successively, I hear them all at once. What a delight this is! All this inventing, this producing, takes place in a pleasing, lively dream.
6. My subject enlarges itself, becomes methodized and define, and the whole, though it be long, stands almost complete and finished in my mind, so that I can survey it, like a fine picture or a beautiful statute, at a glance.
7. I pay no attention whatever to anybody’s praise or blame. I simply follow my own feelings.
8. It is a great consolation for me to remember that the Lord, to whom I had drawn near in humble and child-like faith, has suffered and died for me, and that He will look on me in love and compassion.Requiem Piano Concerto No. 21
Zlata Ognevich – representative of Ukraine at the Eurovision-2013
ZLATA OGNEVICH
Inna Leonidovna Bordyug
(born 12 January 1986, Murmansk, Russian SSR)
Nationality: Ukraine
Category: Celebrities
Occupation: Singer
Specification: She was representating Ukraine at the Eurovision Song Contest 2013, where she won third place with 214 points.
Gender: Female
Height: 5’ 5” (1.65 m)
Weight: 114,7 lbs (52 kg)
Nicknames: “Ukrainian butterfly”, ” Natasha Rostova of our time»
Biography: Her father was a military surgeon and teacher, mother – a teacher of Russian language and literature. During the five years of her father service she lived in Gremikha, West Face (Kola Peninsula), St. Petersburg, Belarus. In 1991, the family moved to Ukraine. Zlata grew up in the Crimean city of Sudak, where she began her musical training, learnt to imitate the sounds of nature, swim and dive. She said that diving was a very good breathing exercise, and then trained her vocal ability. In 18 years, Zlata went to Kiev, where she started her professional singing career.
Education: Ognevich is a graduate of Rheingold M. Glière Music College, Kiev Institute of Music (Department of jazz). Her vocal coach –Tatiana Nicolayevna Rusova
Influenced by: Pyotr Ilyich Tchaikovsky
Zlata’s favorites:
Movies, theater, travel, mountains, Italian and Thai cuisine. Favorite food – Thai soup, salads with olive oil, a place of rest – Cuba, perfume – Laura Biagiotti, dog – labrador, film – “Coffee and Cigarettes” by Jim Jarmusch, the last book she read – “Steve Jobs Biography” , idol – Whitney Houston.
Personality: She is open, sensitive, hard-working, she is distinguished by exceptional high demands on itself, self-criticism and perseverance. “As to my personal life, says Zlata, – I have no time for it. Now I am a free artist.
Career: Ognevich is a soloist of the Ensemble of Song and Dance of the Ukrainian Armed Forces. She sang in a Latin band. She works with composer Mikhail Nekrasov (his composition «Wild Dance» helped a Ukrainian singer Ruslana to win at Eurovision Song Contest 2004).
In 2010, she appeared as a special guest at the international fest “Slavic Bazaar” in Vitebsk.
In 2011, she was the First Prize Winner of the I International Song Contest Crimea Music Fest and won a prize of press.
She was the Voice of campaign TM “Crown» – with song “Passion”
Zlata Ognievich was representing Ukraine at the Eurovision Song Contest in Malmö, Sweden with the song “Gravity”, where she won third place with 214 points.
The top 5 favourites of Eurovision 2013 (according to the bookies).
1. Emmelie De Forest (Denmark), song – “Only Teardrops”.
2. Zlata Ognevich (Ukraine), – “Gravity”.
3. Margaret Berger (Norway),– “I Feed You My Love”.
4. Dina Garipova (Russia), – “What If”.
5. Marco Mengoni (Italy), – “L’Essenziale”.
The top 5 winners of Eurovision 2013
1. Emmelie De Forest (Denmark), song – “Only Teardrops” – (281).
2. Farid Mammadov (Azerbaijan), “Hold Me”- (234).
3. Zlata Ognevich (Ukraine), – “Gravity” – (214).
4. Margaret Berger (Norway),– “I Feed You My Love”- (191).
5. Dina Garipova (Russia), – “What If” – (174).
Ellis Paul Torrance – Father of Modern Creativity
E. PAUL TORRANCE
Ellis Paul Torrance
(October 8, 1915, Milledgeville, Georgia – July 12, 2003, Athens, GA) (Aged 87)
Nationality: United States
Category: Scientists
Occupation: Psychologist, educator.
Specification: He known as the “Father of Modern Creativity”, creator of the Torrance Tests of Creative Thinking (TTCT).
Educational psychology, Psychology of Creativity
Gender: Male
Family: In 1959, at the age of 44, he married Pansy Nigh ( 1913-1988), his nursing student and later a nursing educator and his willing supportive and partner.
Education: Bachelor of Arts (1940) Mercer University, Master’s degree in educational psychology (1944) University of Minnesota, Ph.D. (1951) University of Michigan.
Career: In 1936 he began his teaching career at Midway Vocational High School and in 1937 at Georgia Military College. In 1945, he drafted by U.S. Army and became a counselor of disabled veterans at the University of Minnesota Counseling Bureau. In 1951 he became a director of the Survival Research of the U.S. Air Force in Colorado In 1958, he returned to the University of Minnesota and served as director of the Bureau of Educational Research until 1966. He had been the head of the Educational Psychology Dept (1966 – 1978), and professor (1978 -1984) at the University of Georgia (UGA). He retired from Georgia in 1984. In 1984, the UGA established the Torrance Center for Creativity and Talent Development.
Personality: Torrance had a kind, gentle and generous character. He was an eminence mentor and teacher and always demonstrated the respect and support for his colleagues and students.
Major contributions:
1. Creativity. Torrance devoted his career to teaching and researching creativity. His interest in creativity emerged in 1937 from his observation that many his difficult student went on to become successful in life and work. During his working for the U.S. Air Force (1951-57), he developed his survival definition of creativity, which stated that a courageous risk- taking is essential for creativity.
Later he defines creativity as “…the process of sensing gaps or disturbing, missing elements; forming ideas or hypotheses concerning them; testing these hypotheses; and communicating the results, possibly modifying and retesting the hypotheses” (1962).
2. Torrance Tests of Creative Thinking (TTCT) or Minnesota Tests of Creative Thinking (MTCT).
2.1. Torrance with his collegues invented the most widely known, The Torrance Tests of Creative Thinking, which was published in 1966. Torrance have used many of Guilfords (1950, 1956) concepts in their test construction. but in contrast to Guilford, he sought both verbal and figural activities and grouped the different subtests of the TTCT into three categories: 1. Verbal tasks using verbal stimuli. 2. Verbal tasks using non-verbal stimuli. 3. Non-verbal tasks.
2.2. He developed a benchmark method for quantifying creativity . At the beginning he used use Guilford’s (1956) four divergent thinking factors: 1. Fluency. The total number of interpretable, meaningful, and relevant ideas generated in response to the stimulus. 2.Flexibility. the number of different categories or shifts in responses. 3.Originality. the number of unusual yet relevant ideas and the statistical rarity of the responses. 4. Elaboration. The amount of detail used to extend a response(1966, 1974).
2.3.Then Torrance decided to enhance the scoring of the figural tests. The third edition of the TTCT eliminated the Flexibility scale from the figural test, but added Resistance to Premature Closure and Abstractness of Titles as two new criterion-referenced scores on the figural (1984). Using this system, the figural tests are scored according to five norm referenced scores and 13 criterion referenced scores . So TTCT-Figural form measures five subscales: (1) fluency, (2) originality, (3) elaboration, (4) abstractness of titles and (5) resistance to premature closure.
The criterion-referenced measures include: emotional expressiveness, story-telling articulateness, Movement or actions, expressiveness of titles, syntheses if incomplete figures, synthesis if lines, if circles, unusual visualization, extending or breaking boundaries, humor, richness of imagery, colourfulness of imagery, and fantasy.
2.4. The newest version of the Torrance Test of Creative Thinking (Goff and Torrance, 2002) measured 4 norm-referenced abilities: 1. fluency, ability to produce numerous ideas relating to the activity. 2. originality, ability to produce ideas which are not generally produced. 3. elaboration, ability to embellish ideas relating to the activity. 4. flexibility, ability to interpret similar stimulus in different ways.
2.5. Torrance and his associates administered the Minnesota Tests of Creative Thinking (MTCT) to several thousands of school children. They also completed the 40-year longitudinal study on creativity, done on 215 students that attended two Minneapolis elementary schools from 1958-1964.
Moreover Torrance is aware that the use of the TTCT, is still not able to measure the essence of creativity, that a high degree of the measured creative abilities only increases a person’s chances of behaving creatively.
3. Threshold hypothesis. Torrance proposed popular model is what has come to be known as “the threshold hypothesis”, which holds that, in a general sample, there will be a positive correlation between low creativity and intelligence scores, but a correlation will not be found with higher scores.
4. Future Problem Solving Program. Torrance created the Future Problem Solving Program and developed the Incubation Model of Teaching, which has now expanded and reached over 250,000 students internationally.
This program stimulates critical and creative thinking skills, extend perceptions of the real world, encourages students to develop a vision for the future, Integrate problem solving into the curriculum, offer authentic assessment and prepares students for leadership roles.”
He wrote: “I have always been interested in empowering children, releasing their creative potential. But first I had to measure that potential. So I have a reputation as a psychometrician, but all along I have worked with the development of creativity” (1989).
Awards: Torrance was the recipient of the Arthur Lipper Award of the World Olympics of the Mind for outstanding original contributions to human creativity, an elected member of Who’s Who in the World.
Hew was a veteran of the U.S. Army and a member of Athens First Baptist Church.
Read more: Genvive
Major works:
E. Paul Torrance had a total of 1,871 publications, including 88 books, 256 parts of books or cooperative volumes, 408 journal articles, and 538 reports, 64 forewords, manuals, tests and instruction materials, that have been translated into more than 32 languages.
1. Torrance, E. P. (1962). Guiding creative talent. Englewood Cliffs, NJ: Prentice Hall. 2. Torrance, E. P. (1965). Rewarding Creative Behavior. Experiments in Classroom Creativity. Englewood Cliffs, N. J.: Prentice-Hall, Inc. 3. Torrance, E. P. (1966). 4. Torrance Tests of Creative Thinking: Norms technical manual (Research Edition). Princeton, NJ: Personnel Press. 5. Torrance, E. P. (1974). Norms-technical manual: Torrance Tests of Creative Thinking. Lexington, MA: Ginn and Company. 6. Torrance, E.P. (1974). Torrance Tests of Creative Thinking. Scholastic Testing Service, Inc. 7. Torrance, E. P. (1979). The search for Satori and creativity. New York: Creative Education Foundation. 8. Torrance, E. P., & Safter, H. T. (1990). The Incubation Model: Getting beyond the aha! Buffalo, NY: Bearly. 10. Torrance, E. P., & Safter, H. T. (1999). Making the creative leap beyond. Buffalo, NY: Creative Education Foundation Press. 11. Torrance, E. P., & Sisk, D. A. (1997). Gifted and talented children in the regular classroom. Buffalo, NY: Creative Education Foundation Press. 12. Torrance, E. P. (1994). Creativity: Just wanting to know. Pretoria, Republic of South Africa: Benedic Books. 13. Torrance, E. P. (1995) Why Fly? A philosophy of creativity. Norwood, NJ: Ablex. 14. Torrance, E. P. (2001). Experiences in developing creativity measures: Insights, discoveries, decisions. Manuscript submitted for publication. 15. Goff, K., & Torrance, E. P. (2002). Abbreviated Torrance test for adults manual. Bensenville, IL: Scholastic. Testing Service, Inc.
Adriana Lima – Brazilian Supermodel, Measurements and Best Quotes
 ADRIANA LIMA
ADRIANA LIMA
Adriana Francesca Lima
(June 12, 1981, Salvador da Bahia, Brazil)
Nationality: Brazil
Category: Celebrities
Occupation: Model, Actress
Specification: One of the most famous and in-demand models of the world, one of the Victoria’s Secret’s Perfect 10.
Gender: Female
Eye Color: Blue
Height: 178 cm (5 ft10in)
Weight: 59 kg (130 lb)
Measurements: 89-61-89 (EU); 35-24-35(US)
Religion: Roman Catholic
Husband: Marko Jaric (NBA player, together from 2007, m. 14-Feb-2009, 2009–present)
Daughter – Valentina Lima Jaric (b. 15-Nov-2009)
Adriana Lima quotes: 1. Be sure what you want and be sure about yourself. Fashion is not just beauty, it’s about good attitude. You have to believe in yourself and be strong.
2. We come to love not by finding the perfect person, but by learning to see an imperfect person perfectly… Only after we have lost everything, are we free to do anything… Throw things out there and not be perfect and not have answers to anything and see if people understand.
3. Fashion is about good energy. It’s about feelings. That’s what I have to give the people, good energy and good feelings.
4. I used to be very shy. When I first started, I had to go to a casting, and I had to go in a bikini. I thought I was too skinny. But I went in and got the job! And that’s how I started.
5. Don’t try to be what you’re not. If you’re nervous, be nervous. If you’re shy, be shy. It’s cute.
6. If you ask people what they’ve always wanted to do, most people haven’t done it. That breaks my heart.
7. I don’t like fights. I don’t like aggressive people.




Joy Paul Guilford – One of the founders of the Psychology of Creativity
 JOY PAUL GUILFORD
JOY PAUL GUILFORD
(March 7, 1897, Marquette, Nebraska, USA – November 26, 1987, Los Angeles) (Aged 90)
Nationality: United States
Category: Scientists
Occupation: Psychologist
Specification: Author of a three-dimensional model of the intellect and the concept of the Divergent Thinking. Applied psychology: psychometrics. One of the founders of the Psychology of Creativity.
Gender: Male
Family: His wife – Ruth, his daughter – Joan S. McGuire (Author of the book about her father “An Odyssey of the SOI Mode”).
Education: Guilford graduated from the University of Nebraska. (1918-1924). In 1924 he entered the psychology Ph.D. program at Cornell University, where he studied under Edward Titchener and Kurt Koffka. He was awarded the Ph.D. in 1927.
Career: Guilford taught at the University of Kansas (1927 – 1928), worked as Associate Professor at University of Nebraska (1928 – 1940) and Psychology professor at the University of Southern California (1940 – 1967). In 1941 he entered the U.S. Army and served as Director of Psychological Research Unit No. 3 at Santa Ana Army Air Base.
Major contributions:
1. Structure of Intellect (SOI) or (SI): three-dimensional model.
Guilford proposed that intelligence is not a unitary concept and introduced a three-dimensional theoretical model of the Structure of the intellect, according to which the intellect may be represented by three aspects:
– operation (cognition, memory, divergent production, convergent production, evaluation),
– products (units, classes, relations, systems, transformations, and implications),
– content (visual, auditory, symbolic, semantic, behavioral).
The 5 x 6 x 5 figure provides 150 possible abilities (1955). The final version of the SOI model (1988) was resembled as a cube with 3 dimesions, or 6 x 5 x 6 figure. In this model Guilford introduced some new operations (cognition, memory recording, memory retention, convergent production, divergent production, and evaluation). That yields 180 possible unique abilities, which are correlated with each other.
2. Creativity. Guilford in his 1950 American Psychological Association (APA) presidential address emphasized the central significance of creative talent for industry, science, arts and education and the need for more research into the nature of creativity. He developed a theory of creativity, in which he described creativity as sensitivity to problems (1950); as divergent thinking and ability to generate multiple ideas (1959), creation of new patterns, a transformation of knowledge and meaning or use the functions of objects in a new way (1962, 1967).
3. Divergent thinking. Guilford first proposed the concept of Divergent Thinking in the 1950s and later introduced its developed model as the main ingredient of creativity (1976). Thus he directly associated divergent thinking with creativity, appointing it several characteristics:
1. Fluency (the ability to produce great number of ideas or problem solutions).
2. Flexibility (the ability to simultaneously propose a variety of approaches to a specific problem).
3. Originality (the ability to produce new, original ideas).
4. Elaboration (the ability to systematize and organize the details of an idea in a head and carry it out).
He also emphasized the distinction between convergent and divergent thinking.
4. Psychometric study of human intelligence. Guilford is one of the leaders of the psychometric school of research on intelligence, creativity and personality. He was a pioneer in the development of a system of psychological tests for the study of productive thought and creative abilities of the individual. He designed numerous tests that measured divergent or creative thinking and the intellectual ability of creative people.
Guilford’s methods have been widely used with the practical aim of identifying the creative potentialities of engineers and scientific workers and gifted students.
5. Honors and awards: President of the Psychometric Society(1938); President of the Western Psychological Association (1946); President of the American Psychological Association (1949); Doctor of Laws (University of Nebraska.1952); PhD, Sociology (University of Southern California, 1962), Gold Medal of the American Psychological Foundation (1983).
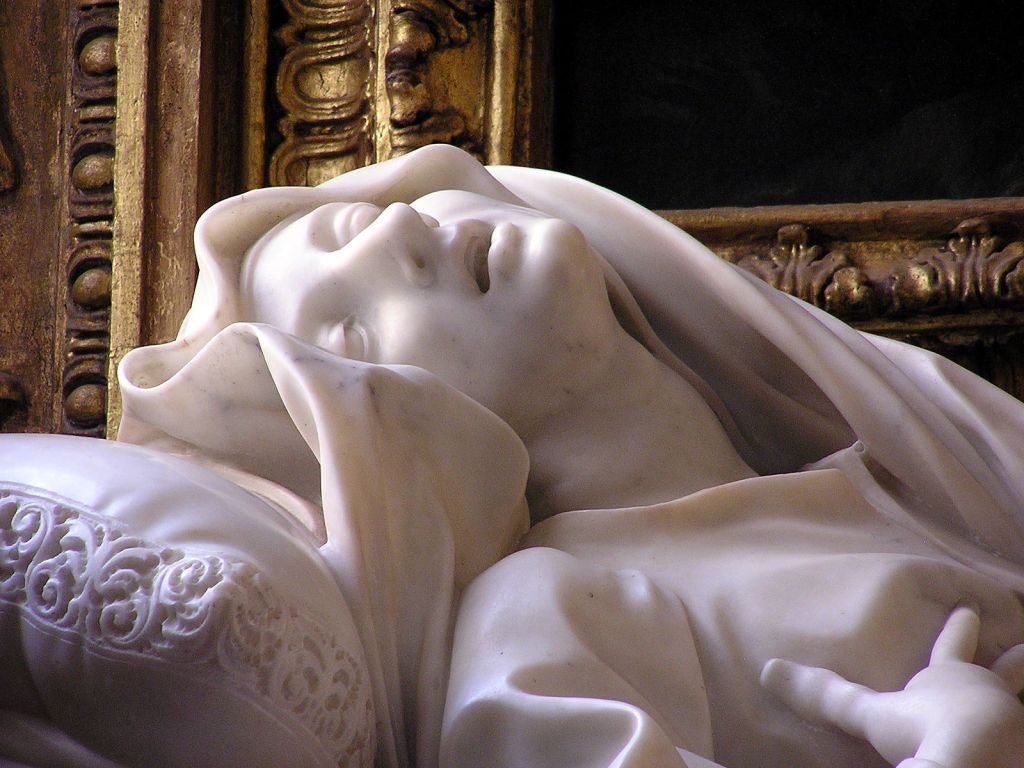
Gian Lorenzo Bernini – Great Italian sculptor and architect
GIAN BERNINI
Gian (Giovanni) Lorenzo Bernini
7 December 1598, Naples, Italy — 28 November 1680, Rome) (aged 81)
Nationality: Italy
Category: Art workers
Occupation: Sculptor, architect, painter.
Specification: Founder of the Baroque style of architecture and sculpture, the greatest sculptor-architect of his time.
Gender: Male
Religion: Roman Catholic
Gian Bernini Quotes:
1. Three things are needed for success in painting and sculpture: to see beauty when young and accustom oneself to it, to work hard, and to obtain good advice.
2. An architect proves his skill by turning the defects of a site into advantages. 3. There are two devices which can help the sculptor to judge his work: one is not to see it for a while. The other… is to look at his work through spectacles which will change its color and magnify or diminish it, so as to disguise it somehow to his eye, and make it look as though it were the work of another…


Sigmund Freud – Founder of Psychoanalysis
SIGMUND FREUD
Sigismund Shlomo Freud
(May 6, 1856, Freiberg, Austro-Hungary (now Příbor, Czech Republic) – September 23, 1939, London, England) (aged 83)
Nationality: Austria
Category: Scientists
Occupation: Psychologist, psychiatrist
Specification: Founder of Psychoanalysis. He made a tremendous impact on psychology, psychotherapy, art and on the culture in general.
Gender: Male
Parents: His father Jakob, a wool merchant, was 41 and his mother Amalié (née Nathansohn), the third wife of Jakob, was 21. Sigmund was the first of eight children in the family
Education: Freud went to the University of Vienna aged 17. He received his M.D. degree in 1881 at the age of 25.
Influences: Brentano, Breuer, Darwin, Hartmann, Schopenhauer, Nietzsche, Shakespeare, Goethe, Dostoyevsky.
In 1886 Freud resigned his hospital post, entered private practice specializing in “nervous disorders” and married Martha Bernays, the granddaughter of Isaac Bernays, a Chief Rabbi in Hamburg. The couple had six children
Freud battled mouth cancer the last several years of his life, but continued to smoke cigars.
With Nazi occupation of Austria in 1938 Freud with his wife and daughter fled to England. Four of Freud’s five sisters died in concentration camps.
Major contributions:
1. Theory of Psychoanalysis and fundamental concepts of Depth Psychology which are based on:
a) theory of the unconscious mind (also he didn’t invent this idea, but put it into clinical practice and made it popular). He wrote: “The mind is like an iceberg, it floats with one-seventh of its bulk above water’; b) statement that libido or sexual instinct and desire (Eros or libido) is the primary motivational energy of human life and later in Beyond the Pleasure Principle (1920)- death drive (Thanatos) was added; c) theory of sublimation, as the process of deflecting sexual instincts into acts of higher social valuation; d) interpretation of dreams as sources of insight into unconscious desires. Freud called dreams the “royal road to the unconscious”. Dream mechanisms: condensation, displacement, identification, composition, inversion, secondary elaboration; e) “repression” as the key factor in the operation of the unconscious and defence mechanism, which together with other mechanisms (denial, idealization, splitting, identification, rationalization) to manipulate, deny, or distort reality for protect the ego; f) theory of unconscious primary process and conscious secondary process; g) Economic, homeostatic model of the psyche, tendency of mental apparatus “to keep as low as possible the total amount of the excitations”.
2. Topology of the psyche. In 1899 Freud developed his first topology of the psyche or previous topographic schema: conscious, unconscious, and preconscious. In his later work (1920, 1923), he proposed that the human psyche could be divided into three parts: ego which operates on the Reality Principle, super-ego (a moral component of the psyche), and Id, which operates on the Pleasure Principle, satisfying urges for food and sex. “The ego is not master in its own house”.
3. Development of psychics. a) Personality is developed by the person’s childhood experiences; b) personality develops during childhood through a series of psychosexual stages: 1) oral (birth-1 year), 2) anal (1-3), 3) phallic (3-6), 4) latent (6-12). 5) genital (12 -); c) the stage at which a person becomes fixated in childhood has a decisive influence on adult personality; d) Oedipus complex – boys passed through the phallic stage in which they fixated on the mother as a sexual object and on the father as a rival (In girls – Electra complex).
4. Clinical practice of psychoanalysis. a) Freud created the clinical practice of psychoanalysis as dialogue between a patient and a psychoanalyst or “talking cure”; b) the goal of psychoanalysis, was to bring subconsciously repressed thoughts and feelings into consciousness in order to free the patient from painful thoughts and feelings. “Where id was, their ego shall be”; c) major points of Freudian therapy: Relaxed atmosphere, resistance, transference, catharsis, insight; d) he developed the therapeutic techniques, including the use of Free association and Dream analysis. Freud wrote: “Analysis does not set out to make pathological reactions impossible, but to give the patient’s ego freedom to decide one way or another”.
5. Culture. Freud as materialist and naturalist conceived civilization basically in terms of the basic human instinct or drive.
“It is impossible to overlook the extent to which civilization is built upon a renunciation of instinct”.
6. Religion. Freud maintained that “Religion is an illusion and it derives its strength from the fact that it falls in with our instinctual desires’. He perceived religion, with its suppression of man’s violent nature, restraint of the death drive, aggression and violence,
7. Creativity. a) Creativity is identified with the work of the unconscious, with the manifestation of the energy of the id and the power of libido by means of most beneficial defence mechanism- sublimation; b) Freud, following Schiller, wrote that we can gain access to “involuntary ideas” by relaxing our rational control over the imagination; c) fantasies is considered as Fulfilments of ambitious and erotic wishes, as an escape from inner conflict, as a “neutral zone”, free space of pure imagination; d) creative writer is borderline neurotics and creativity is a substitute for neurotic symptoms; e) there is a strong analogy between artistic creation, child’s play, dreams, day-dreaming, fantasy and humour.
Freud remains one of the most influential figures in today’s psychology. Many modern psychotherapists follow Freud’s approach, even if they reject his theories.
Freud quotes: 1. Love and work… work and love, that’s all there is. 2. Sometimes a cigar is just a cigar. 3. Civilization began the first time an angry person cast a word instead of a rock.
Melinda Gates – Co-chair of the Bill & Melinda Gates Foundation
Melinda French Gates
(born Melinda Ann French)
(August 15, 1964, Dallas, Texas, USA)
Nationality: United States
Category: Votaries of Spirit and Humanity
Occupation: Philanthropist, businesswoman
Specification: Co-founder and co-chair of the Bill & Melinda Gates Foundation.
Gender: Female
Religion: Roman Catholic
Residence: Medina, WA, near Seattle.
Education: She earned a bachelor’s degree in computer science and economics from Duke University in 1986 and an Master of Business Administration, Duke University Fuqua School of Business in 1987.
Family: Father-Raymond Joseph French, Jr., an engineer and mother- Elaine Agnes Amerland French a homemaker (from Germany). Melinda was 16 when her father brought home the first Apple III computer.
Spouse – Bill Gates, 2nd Richest Man in the World (Net Worth $66 Billion as of Sept. 2012). They met in 1987 at a Microsoft press event in Manhattan. On 1st of January, 1994, she married Bill Gates in a private ceremony held in Lanai, Hawaii.
Children: Melinda and Bill Gates have three children: daughters Jennifer Katharine Gates (b. 26 April 1996) and Phoebe Adele Gates (b. 2002), and son Rory John Gates (b. 23 May1999).
Contributions:
1. In 1987 she joined Microsoft Corp. and distinguished herself in business as a unit manager and leader in the development of Microsoft’s multimedia products.
2. In 1996, M. Gates retired from her position as Microsoft’s General Manager of Information Products.
3. She is a former member of the board of trustees of Duke University (1996 to 2003) and is a former co-chair of the Washington State Governor’s Commission on Early Learning.
4. Melinda is Co-founder and co-chair of the largest transparently operated private foundation in the world, which was formed in 1994 and renamed the Bill & Melinda Gates Foundation (B&MGF) in 1999. The basic Values of the foundation are: Optimism, Collaboration, Rigor, Innovation and the primary aims are, in the world to enhance healthcare and reduce extreme poverty, and in America, to expand educational opportunities and access to information technology, improve public libraries and support at-risk families.
As of 2009, Melinda and Bill Gates have donated more than US$24 billion to the Foundation. And as of 2011 it had an endowment of US$33.5 billion andas of 2012- $37.6 billion.
Awards:
In December 2005, Melinda and Bill Gates were named by Time as Persons of the Year alongside Bono.
In 2006 Melinda and Bill Gates received the Spanish Prince of Asturias Award for International Cooperation and Order of the Aztec Eagle for their philanthropic work around the world in the areas of health and education.
In May 2006, she was honored for her work to improve the lives of children locally and around the world.
She and her husband, Bill Gates, were both awarded the 2010 «J. William Fulbright» Prize for International Understanding.
Melinda Gates was ranked list of the 100 Most Powerful Women, #12 in Forbes in 2006, #24 in 2007, #40 2008 and #4 in 2012.
Quotes by Melinda Gates: “Our desire to bring every good thing to our children is a force for good throughout the world. It’s what propels societies forward.”
Mark Zuckerberg – Co-Founder, CEO, President of Meta Platforms (Facebook)
Mark Elliot “Zuck” Zuckerberg
(May 14, 1984, White Plains, New York, USA)
Nationality: United States
Category: Figures
Occupation: Businessperson, Computer Programmer, Inventor.
Specification: Co-Founder, CEO & President of Meta Platforms (formerly Facebook, Inc.)
Gender: Male
Net worth: US$6.9 billion (2010)
US$ 117,9 billion (2023)
Education: Harvard University (dropped out)
Personal life:
On May 19, 2012, he married Priscilla Chan (born February 24, 1985) an American philanthropist and a former pediatrician.
On July 31, 2015, Zuckerberg revealed they were expecting a baby girl and that Chan had previously experienced three miscarriages.
Their daughter, Maxima Chan Zuckerberg (Chinese name is Chen Mingyu ) was born on December 1, 2015.
heir second daughter, August, was born in August 2017.
Zuckerberg and his wife welcomed their third daughter Aurelia on March 24, 2023.
The couple also have a Puli dog named Beast,[192] who has over two million followers on Facebook.[193]
Elton John – a British singer, Pop superstar and Composer
ELTON JOHN
Sir Elton Hercules John
born Reginald Kenneth Dwight
( March 25, 1947, Pinner, Middlesex, England)
Nationality: England
Category: Celebrities
Occupation: Singer, actor, composer
Specification: The biggest pop superstar of the early ’70s.
Genres: Rock, pop, glam rock, soft rock
Gender: Male
Representative Albums: “Honky Chateau”, “Captain Fantastic and the Brown Dirt Cowboy”, “Greatest Hits, Vol. 2”
First Major Screen Credit: Friends” (1971).
Elton John has more than fifty top-40 hits on the UK Singles Chart and US Billboard Hot 100, including nine number ones in both countries, as well as seven consecutive number-one albums in the US.
He has sold over 300 million records worldwide, making him one of the best-selling music artists of all time.
John’s numerous awards include five Grammy Awards, five Brit Awards; including for Outstanding Contribution to Music; two Academy Awards. Music awards include the Academy Award for Best Original Song for “Can You Feel the Love Tonight” from The Lion King, the 1994 .
The 2019 Golden Globe Award for Best Original Song and Academy Award for Best Original Song both went to John for “(I’m Gonna) Love Me Again”, shared with Taupin.
He is also the recipient of such honors as two Golden Globes, a Tony Award, a Laurence Olivier Award, a Disney Legend Award, and the Kennedy Center Honor.
He was inducted into the Songwriters Hall of Fame in 1992 and the Rock and Roll Hall of Fame in 1994.




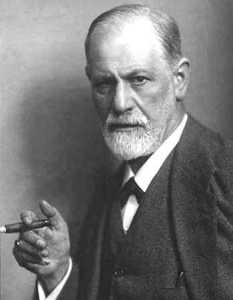



You must be logged in to post a comment.